MySQL has built-in functionality that allows you to log SQL queries to a file , You can enable the full SQL queries logs to a file or only slow running queries log. It is easy for us to troubleshoot/ debug the sql statement if SQL queries log enable , The slow query log is used to find queries that take a long time to execute and are therefore candidates for optimization.
To enable you just need to add some lines to your my.cnf file, and restart. Add the following:
* To enable slow Query Log only
log-slow-queries = /var/log/mysql/mysql-slow.log
long_query_time = 1
After enabling slow query, mysqld writes a statement to the slow query log file and it consists of all SQL statements that took more than long_query_time seconds to execute. The time to acquire the initial table locks is not counted as execution time. mysqld only log after SQL statements has been executed and after all locks have been released, so log order might be different from execution order. The minimum and default values of long_query_time are 1 and 10, respectively.
* To enable full Log Query
log=/var/log/mysqldquery.log
The above will log all queries to the log file.
Selecting Queries to Optmize
• The slow query log
– Logs all queries that take longer than long_query_time
– Can also log all querie s that don’t use indexes with
--log-queries-not-using-indexes
– To log slow administatve commands use
--log-slow-admin-statements
– To analyze the contents of the slow log use
mysqldumpslow
Subscribe to:
Post Comments (Atom)
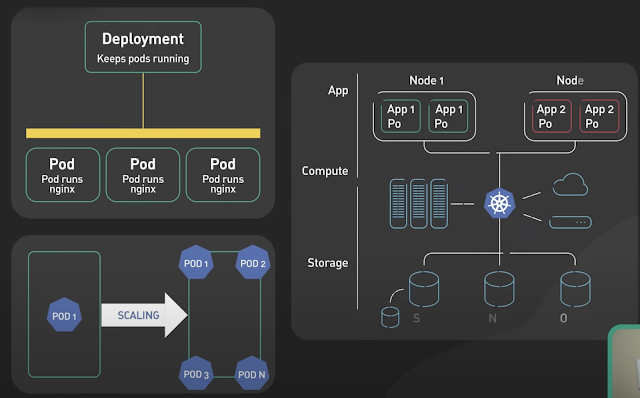
Basics of Kubernetes
Kubernetes, often abbreviated as K8s , is an open-source platform designed to automate the deployment, scaling, and management of container...
-
The Unix top command is designed to help users determine which processes are running and which applications are using more memory or process...
-
IOPS (input/output operations per second) is the standard unit of measurement for the maximum number of reads and writes to non-contiguous ...
-
MySQL's InnoDB storage engine data refresh every situation. This post from InnoDB down, look at the data from the memory to the InnoDB ...


1 comment:
If you finally have a mysql slow query log and want to analyze it, you should check out http://github.com/wvanbergen/request-log-analyzer
Post a Comment