you wanted to delete all the files in a directory that begins with the word 'temp' bala bala
[prabhat@my-site]# rm temp*
bash: /bin/rm: Argument list too long
ERROR!
This happens when you are trying to delete too many files in a directory at the same time - it seems rm has limits ....
To solve the problem:
Use 'find' to pipe all the matching files to 'rm', one at a time.
[prabhat@my-site]# find . -name 'temp*' | xargs rm
or
[prabhat@my-site]# find . -name 'temp*' - print0 | xargs -0 rm -f
Tuesday, December 26, 2006
Monday, December 18, 2006
Sort folders by size with one command
Entire user’s data is under /home, I need to have a list of all the sub folders sorted by the size of the sub folders.
simple command to get the list of sub folders sorted by their size:
du --max-depth=1 /home/ | sort -n -r
simple command to get the list of sub folders sorted by their size:
du --max-depth=1 /home/ | sort -n -r
Friday, December 01, 2006
Zombie Process
A process can be sleeping in kernel code. Usually that's because of faulty hardware or a badly written driver- or maybe a little of both. A device that isn't set to the interrupt the driver thinks it is can cause this, for example- the driver is waiting for something its never going to get. The process doesn't ignore your signal- it just never gets it.
A zombie process doesn't react to signals because it's not really a process at all- it's just what's left over after it died. What's supposed to happen is that its parent process was to issue a "wait()" to collect the information about its exit. If the parent doesn't (programming error or just bad programming), you get a zombie. The zombie will go away if its parent dies- it will be "adopted" by init which will do the wait()- so if you see one hanging about, check its parent; if it is init, it will be gone soon, if not the only recourse is to kill the parent..which you may or may not want to do.
* Finally, a process that is being traced (by a debugger, for example) won't react to the KILL either.
We can find out zombie process by :-
Use top or ps command:
# top
OR
# ps aux | awk '{ print $8 " " $2 }' | grep -w Z
How do I kill zombie process?
You cannot kill zombies, as they are already dead. But if you have too many zombies then kill parent process or restart service.
You can kill zombie process using PID obtained from any one of the above command. For example kill zombie proces having PID 4104:
# kill -9 4104
*Please note that kill -9 does not guarantee to kill a zombie process
How do I automate zombie process killing?
Write a script and schedule as a cron job.
for each in `ps jauxww | grep Z | grep -v PID | awk ‘{print $3}’`; do for every in `ps auxw | grep $each | grep cron | awk ‘{print $2}’`; do kill -9 $every; done; done
A zombie process doesn't react to signals because it's not really a process at all- it's just what's left over after it died. What's supposed to happen is that its parent process was to issue a "wait()" to collect the information about its exit. If the parent doesn't (programming error or just bad programming), you get a zombie. The zombie will go away if its parent dies- it will be "adopted" by init which will do the wait()- so if you see one hanging about, check its parent; if it is init, it will be gone soon, if not the only recourse is to kill the parent..which you may or may not want to do.
* Finally, a process that is being traced (by a debugger, for example) won't react to the KILL either.
We can find out zombie process by :-
Use top or ps command:
# top
OR
# ps aux | awk '{ print $8 " " $2 }' | grep -w Z
How do I kill zombie process?
You cannot kill zombies, as they are already dead. But if you have too many zombies then kill parent process or restart service.
You can kill zombie process using PID obtained from any one of the above command. For example kill zombie proces having PID 4104:
# kill -9 4104
*Please note that kill -9 does not guarantee to kill a zombie process
How do I automate zombie process killing?
Write a script and schedule as a cron job.
for each in `ps jauxww | grep Z | grep -v PID | awk ‘{print $3}’`; do for every in `ps auxw | grep $each | grep cron | awk ‘{print $2}’`; do kill -9 $every; done; done
Thursday, November 23, 2006
grep command : Finds text within a file
The grep command searches for the pattern specified by the Pattern parameter and writes each matching line to standard output.
Examples
0. $ grep '12.00' /home/prabhat/backup/log.txt
This command basically shows how you can use grep to extract lines containing a particular string from a text file.
1. To use a pattern that contains some of the pattern-matching characters *, ^, ?, [, ], \(, \), \{, and \}, enter:
grep "^[a-zA-Z]" pgm.s
This displays every line in pgm.s whose first character is a letter.
2. To display all lines that do not match a pattern, enter:
grep -v "^#" pgm.s
This displays every line in pgm.s whose first character is not a # (pound sign).
3. To display all lines in the file1 file that match either the abc or xyz string, enter:
grep -E "abc|xyz" file1
4. To search for a $ (dollar sign) in the file named test2, enter:
grep \\$ test2
The \\ (double backslash) characters are necessary in order to force the shell to pass a \$ (single backslash, dollar sign) to the grep command. The \ (single backslash) character tells the grep command to treat the following character (in this example the $) as a literal character rather than an expression character. Use the fgrep command to avoid the necessity of using escape characters such as the backslash.
^ - match at the beginning of the line
$ - match at the end of the line
Some extra options for grep
-v
Reverses the normal behavior of the grep command - Instead of selecting lines, it rejects the lines that match the given criteria.
-c
It suppresses the normal output and only prints the total count of matching lines instead of the actual lines.
-i
Ignores the case of the text when matching the given pattern.
-w
Checks if the given pattern is a word by itself and not a part of another word. Thus if you search for 'bay' and the word 'baywatch' is present in a file, the particular line containing that word would not be returned in the result.
-l
Only gives the names of the files in which the given pattern was found.
-r
Checks for the given pattern , recursively within the directory that you specify after the -r option
know more
http://www.computerhope.com/unix/ugrep.htm
http://linux.about.com/od/commands/l/blcmdl1_grep.htm
http://www.lowfatlinux.com/linux-grep-manual.html
Examples
0. $ grep '12.00' /home/prabhat/backup/log.txt
This command basically shows how you can use grep to extract lines containing a particular string from a text file.
1. To use a pattern that contains some of the pattern-matching characters *, ^, ?, [, ], \(, \), \{, and \}, enter:
grep "^[a-zA-Z]" pgm.s
This displays every line in pgm.s whose first character is a letter.
2. To display all lines that do not match a pattern, enter:
grep -v "^#" pgm.s
This displays every line in pgm.s whose first character is not a # (pound sign).
3. To display all lines in the file1 file that match either the abc or xyz string, enter:
grep -E "abc|xyz" file1
4. To search for a $ (dollar sign) in the file named test2, enter:
grep \\$ test2
The \\ (double backslash) characters are necessary in order to force the shell to pass a \$ (single backslash, dollar sign) to the grep command. The \ (single backslash) character tells the grep command to treat the following character (in this example the $) as a literal character rather than an expression character. Use the fgrep command to avoid the necessity of using escape characters such as the backslash.
^ - match at the beginning of the line
$ - match at the end of the line
Some extra options for grep
-v
Reverses the normal behavior of the grep command - Instead of selecting lines, it rejects the lines that match the given criteria.
-c
It suppresses the normal output and only prints the total count of matching lines instead of the actual lines.
-i
Ignores the case of the text when matching the given pattern.
-w
Checks if the given pattern is a word by itself and not a part of another word. Thus if you search for 'bay' and the word 'baywatch' is present in a file, the particular line containing that word would not be returned in the result.
-l
Only gives the names of the files in which the given pattern was found.
-r
Checks for the given pattern , recursively within the directory that you specify after the -r option
know more
http://www.computerhope.com/unix/ugrep.htm
http://linux.about.com/od/commands/l/blcmdl1_grep.htm
http://www.lowfatlinux.com/linux-grep-manual.html
Wednesday, November 22, 2006
yum : Yellow dog Updater, Modified
automated software installation and update for linux
yum is software installation tool for Red hat linux and Fedora Linux. It is a complete software management system. yum is designed to use over network/internet. It does not use CDROM to install packages. If you are using fedora you don't have to install it, it is part of fedora itself.
In the case u don't have yum, then u can download yum from project home page http://linux.duke.edu/projects/yum/download.ptml
u can Install using.(it is avaliable in rmp)
# rpm -ivh yup*
U can Configure yum editing /etc/yum.conf
# emacs /etc/yum.conf
Append or edit code as follows:
[base]
name=Fedora Core $releasever - $basearch - Base
baseurl=http://apt.sw.be/fedora/$releasever/en/$basearch/dag
baseurl=http://mirrors.kernel.org/fedora/core/$releasever/$basearch/os
Install GPG signature key with rpm command:
# rpm --import http://dag.wieers.com/packages/RPM-GPG-KEY.dag.txt
and other keys too (if any using above command)
Update your package list:
# yum check-update
Install a new package called test
# yum install test
To update packages
# yum update
To update a single package called test1
# yum update test1
To remove a package called test2
# yum remove test2
To list all packages
# yum list installed
You can search using grep command
# yum list installed | grep test1
Display information on a package called test
# yum info test
To display list of packages for which updates are available
# yum list updates
To clean all cahced packages:
# yum clean packages
To remove all cached packages and old headers:
# yum clean all
Force a fresh download of package
yum clean headers
yum clean oldheaders
To Know more visit :
http://www.die.net/doc/linux/man/man5/yum.conf.5.html http://www.linuxcommand.org/man_pages/yum8.html
http://www.linuxmanpages.com/man8/yum.8.php
yum is software installation tool for Red hat linux and Fedora Linux. It is a complete software management system. yum is designed to use over network/internet. It does not use CDROM to install packages. If you are using fedora you don't have to install it, it is part of fedora itself.
In the case u don't have yum, then u can download yum from project home page http://linux.duke.edu/projects/yum/download.ptml
u can Install using.(it is avaliable in rmp)
# rpm -ivh yup*
U can Configure yum editing /etc/yum.conf
# emacs /etc/yum.conf
Append or edit code as follows:
[base]
name=Fedora Core $releasever - $basearch - Base
baseurl=http://apt.sw.be/fedora/$releasever/en/$basearch/dag
baseurl=http://mirrors.kernel.org/fedora/core/$releasever/$basearch/os
Install GPG signature key with rpm command:
# rpm --import http://dag.wieers.com/packages/RPM-GPG-KEY.dag.txt
and other keys too (if any using above command)
Update your package list:
# yum check-update
Install a new package called test
# yum install test
To update packages
# yum update
To update a single package called test1
# yum update test1
To remove a package called test2
# yum remove test2
To list all packages
# yum list installed
You can search using grep command
# yum list installed | grep test1
Display information on a package called test
# yum info test
To display list of packages for which updates are available
# yum list updates
To clean all cahced packages:
# yum clean packages
To remove all cached packages and old headers:
# yum clean all
Force a fresh download of package
yum clean headers
yum clean oldheaders
To Know more visit :
http://www.die.net/doc/linux/man/man5/yum.conf.5.html http://www.linuxcommand.org/man_pages/yum8.html
http://www.linuxmanpages.com/man8/yum.8.php
Thursday, November 16, 2006
Did u know how many virtual web site's ?
Following command show how many virtual web site's running on ur server.
httpd -t -D DUMP_VHOSTS
or
apache2 -t -D DUMP_VHOSTS
httpd -t -D DUMP_VHOSTS
or
apache2 -t -D DUMP_VHOSTS
Saturday, November 11, 2006
How to keep a computer from answering to ping?
it is possible to block pings entirely to your machine..
a simple
"echo 1 > /proc/sys/net/ipv4/icmp_echo_ignore_all" will do the trick...
to turn it back on, simply
"echo 0 > /proc/sys/net/ipv4/icmp_echo_ignore_all"
a simple
"echo 1 > /proc/sys/net/ipv4/icmp_echo_ignore_all" will do the trick...
to turn it back on, simply
"echo 0 > /proc/sys/net/ipv4/icmp_echo_ignore_all"
Saturday, October 28, 2006
How to do backup with tar?
You can mantain a list of files that you with to backup into a file and tar
it when you wish.
tar czvf tarfile.tar.gz -T list_file
where list_file is a simple list of what you want to include into the tar
i.e:
/etc/smb.conf
/root/myfile
/etc/ppp (all files into the /etc/ppp directory)
/opt/gnome/html/gnome-dev-info.html
it when you wish.
tar czvf tarfile.tar.gz -T list_file
where list_file is a simple list of what you want to include into the tar
i.e:
/etc/smb.conf
/root/myfile
/etc/ppp (all files into the /etc/ppp directory)
/opt/gnome/html/gnome-dev-info.html
How to remove a file with a dash as first character?
If you accidentally created a file with a - in the beginning then you want to
remove it, you have to do :
rm ./-thefile
remove it, you have to do :
rm ./-thefile
Tuesday, September 26, 2006
Secure Deletion of Data from Magnetic and Solid-State Memory
Secure Deletion of Data from Magnetic and Solid-State Memory
`shred': Remove files more securely
`shred' overwrites devices or files, to help prevent even very
expensive hardware from recovering the data.
Ordinarily when you remove a file (*note rm invocation::), the data
is not actually destroyed. Only the index listing where the file is
stored is destroyed, and the storage is made available for reuse.
There are undelete utilities that will attempt to reconstruct the index
and can bring the file back if the parts were not reused.
On a busy system with a nearly-full drive, space can get reused in a
few seconds. But there is no way to know for sure. If you have
sensitive data, you may want to be sure that recovery is not possible
by actually overwriting the file with non-sensitive data.
The best way to remove something irretrievably is to destroy the
media it's on with acid, melt it down, or the like. For cheap
removable media like floppy disks, this is the preferred method.
However, hard drives are expensive and hard to melt, so the `shred'
utility tries to achieve a similar effect non-destructively.
`Secure Deletion of Data from Magnetic and Solid-State Memory', from the
proceedings of the Sixth USENIX Security Symposium (San Jose,
California, 22-25 July, 1996).
visit: http://www.cs.auckland.ac.nz/~pgut001/pubs/secure_del.html
So. `shred' a linux command : Remove files more securely
shred [OPTION]... FILE[...]
look man page how to use..
`shred': Remove files more securely
`shred' overwrites devices or files, to help prevent even very
expensive hardware from recovering the data.
Ordinarily when you remove a file (*note rm invocation::), the data
is not actually destroyed. Only the index listing where the file is
stored is destroyed, and the storage is made available for reuse.
There are undelete utilities that will attempt to reconstruct the index
and can bring the file back if the parts were not reused.
On a busy system with a nearly-full drive, space can get reused in a
few seconds. But there is no way to know for sure. If you have
sensitive data, you may want to be sure that recovery is not possible
by actually overwriting the file with non-sensitive data.
The best way to remove something irretrievably is to destroy the
media it's on with acid, melt it down, or the like. For cheap
removable media like floppy disks, this is the preferred method.
However, hard drives are expensive and hard to melt, so the `shred'
utility tries to achieve a similar effect non-destructively.
`Secure Deletion of Data from Magnetic and Solid-State Memory', from the
proceedings of the Sixth USENIX Security Symposium (San Jose,
California, 22-25 July, 1996).
visit: http://www.cs.auckland.ac.nz/~pgut001/pubs/secure_del.html
So. `shred' a linux command : Remove files more securely
shred [OPTION]... FILE[...]
look man page how to use..
Monday, September 25, 2006
Danger of 'Ctrl+C' on the Web
We do copy various data by ctrl+c for pasting elsewhere. This copied data is stored in clipboard and is accessible from the net by a combination of Javascripts and ASP.
Just try this:
1) Copy any text by 'ctrl+c'
2) Click the Link: www.sourcecodesworld.com/special/clipboard.asp
You will see the text you copied on the Screen which was accessed by this web page. (Check it out !!)
Do not keep sensitive data (like passwords, reditcard numbers, PIN etc.) in the clipboard while surfing the web. It is extremely easy to extract the text stored in the clipboard to steal your sensitive information.
Be cautious ...
To avoid Clipboard Hack Problem, do the following:
1) In Internet Explorer, Go to Tools -> Internet options -> Security
2) Press Custom level.
3) In the security settings, select disable under Allow paste operations via script and click on 'OK. (Now the contents of your clipboard are safe.)
It doesn't work on firefox.
Happy Surfing......
Just try this:
1) Copy any text by 'ctrl+c'
2) Click the Link: www.sourcecodesworld.com/special/clipboard.asp
You will see the text you copied on the Screen which was accessed by this web page. (Check it out !!)
Do not keep sensitive data (like passwords, reditcard numbers, PIN etc.) in the clipboard while surfing the web. It is extremely easy to extract the text stored in the clipboard to steal your sensitive information.
Be cautious ...
To avoid Clipboard Hack Problem, do the following:
1) In Internet Explorer, Go to Tools -> Internet options -> Security
2) Press Custom level.
3) In the security settings, select disable under Allow paste operations via script and click on 'OK. (Now the contents of your clipboard are safe.)
It doesn't work on firefox.
Happy Surfing......
Friday, September 22, 2006
Recover from rm
In order to undelete a file, you must know the following things:
• On which device your file was stored
• What kind of file system was used (eg. ext2, reiserFS, vfat)
To find it out, type 'mount | column -t'
Or
echo "DEVICE DIRECTORY FS-TYPE" > tmp; mount | cut -d" " -f1,3,5 | sort >> tmp; cat tmp | column -t | sed -e "1s/.*/`tput smso`&`tput rmso`/"
The output should be something like this:
bash$ mount | column -t
/dev/hda5 on / type ext2 (rw)
proc on /proc type proc (rw)
usbdevfs on /proc/bus/usb type usbdevfs (rw)
devpts on /dev/pts type devpts (rw)
/dev/hda1 on /mnt/windows/C type vfat (rw,noexec,nosuid,nodev)
/dev/hda6 on /mnt/windows/E type vfat (rw,noexec,nosuid,nodev)
/dev/hdc5 on /mnt/oldwin type vfat (rw,noexec,nosuid,nodev)
Now, of which (printed) directory was the directory of your deleted file a subdirectory? E.g. if your file was stored on /home/user , you'll have to look for '/', since no closer match can be found. Found it? Cool, right now it's a piece of cake to find the device on which the file was stored and the filesystem type of the device.
If you really need to undelete a file, that's the way to do it:
grep -a -B[size before] -A[size after] 'text' /dev/[your_partition]
Replace [size before], [size after] and [your_partition] with something meaningfull. Don't know what your partition is? Read the Linux undelete
.g.: If you want to undelete a letter (+- 200 lines) starting with "Hi mum" which was stored on /dev/hda1 you can try:
grep -a -B2 -A200 "Hi mum" /dev/hda1
Make sure you do this as root (System administrator)
• On which device your file was stored
• What kind of file system was used (eg. ext2, reiserFS, vfat)
To find it out, type 'mount | column -t'
Or
echo "DEVICE DIRECTORY FS-TYPE" > tmp; mount | cut -d" " -f1,3,5 | sort >> tmp; cat tmp | column -t | sed -e "1s/.*/`tput smso`&`tput rmso`/"
The output should be something like this:
bash$ mount | column -t
/dev/hda5 on / type ext2 (rw)
proc on /proc type proc (rw)
usbdevfs on /proc/bus/usb type usbdevfs (rw)
devpts on /dev/pts type devpts (rw)
/dev/hda1 on /mnt/windows/C type vfat (rw,noexec,nosuid,nodev)
/dev/hda6 on /mnt/windows/E type vfat (rw,noexec,nosuid,nodev)
/dev/hdc5 on /mnt/oldwin type vfat (rw,noexec,nosuid,nodev)
Now, of which (printed) directory was the directory of your deleted file a subdirectory? E.g. if your file was stored on /home/user , you'll have to look for '/', since no closer match can be found. Found it? Cool, right now it's a piece of cake to find the device on which the file was stored and the filesystem type of the device.
If you really need to undelete a file, that's the way to do it:
grep -a -B[size before] -A[size after] 'text' /dev/[your_partition]
Replace [size before], [size after] and [your_partition] with something meaningfull. Don't know what your partition is? Read the Linux undelete
.g.: If you want to undelete a letter (+- 200 lines) starting with "Hi mum" which was stored on /dev/hda1 you can try:
grep -a -B2 -A200 "Hi mum" /dev/hda1
Make sure you do this as root (System administrator)
Proxy server types and uses for HTTP Server
Proxy server
In an enterprise that uses the Internet, a proxy server is a server that acts as an intermediary between a workstation user and the Internet so that the enterprise can ensure security, administrative control, and caching service. A proxy server is associated with or part of a gateway server that separates the enterprise network from the outside network and a firewall server that protects the enterprise network from outside intrusion.
Proxy servers receive requests intended for other servers and then act to fulfill, forward, redirect, or reject the requests. Exactly which service is carried out for a particular request is based on a number of factors which include: the proxy server's capabilities, what is requested, information contained in the request, where the request came from, the intended destination, and in some cases, who sent the request.
An advantage of a proxy server is that its cache can serve all users. If one or more Internet sites are frequently requested, these are likely to be in the proxy's cache, which will improve user response time. In fact, there are special servers called cache servers. A proxy can also do logging.
HTTP Server (powered by Apache) has proxy server capabilities built in. Activating these services is simply a matter of configuration. This topic explains three common proxy concepts: forward proxy, reverse proxy, and proxy chaining.
Forward proxy :
A forward proxy is the most common form of a proxy server and is generally used to pass requests from an isolated, private network to the Internet through a firewall. Using a forward proxy, requests from an isolated network, or intranet, can be rejected or allowed to pass through a firewall. Requests may also be fulfilled by serving from cache rather than passing through the Internet. This allows a level of network security and lessens network traffic.
A forward proxy server will first check to make sure a request is valid. If a request is not valid, or not allowed (blocked by the proxy), it will reject the request resulting in the client receiving an error or a redirect. If a request is valid, a forward proxy may check if the requested information is cached. If it is, the forward proxy serves the cached information. If it is not, the request is sent through a firewall to an actual content server which serves the information to the forward proxy. The proxy, in turn, relays this information to the client and may also cache it, for future requests.
Reverse proxy
A reverse proxy is another common form of a proxy server and is generally used to pass requests from the Internet, through a firewall to isolated, private networks. It is used to prevent Internet clients from having direct, unmonitored access to sensitive data residing on content servers on an isolated network, or intranet. If caching is enabled, a reverse proxy can also lessen network traffic by serving cached information rather than passing all requests to actual content servers. Reverse proxy servers may also balance workload by spreading requests across a number of content servers. One advantage of using a reverse proxy is that Internet clients do not know their requests are being sent to and handled by a reverse proxy server. This allows a reverse proxy to redirect or reject requests without making Internet clients aware of the actual content server (or servers) on a protected network.
A reverse proxy server will first check to make sure a request is valid. If a request is not valid, or not allowed (blocked by the proxy), it will not continue to process the request resulting in the client receiving an error or a redirect. If a request is valid, a reverse proxy may check if the requested information is cached. If it is, the reverse proxy serves the cached information. If it is not, the reverse proxy will request the information from the content server and serve it to the requesting client. It also caches the information for future requests.
Proxy chaining
A proxy chain uses two or more proxy servers to assist in server and protocol performance and network security. Proxy chaining is not a type of proxy, but a use of reverse and forward proxy servers across multiple networks. In addition to the benefits to security and performance, proxy chaining allows requests from different protocols to be fulfilled in cases where, without chaining, such requests would not be possible or permitted. For example, a request using HTTP is sent to a server that can only handle FTP requests. In order for the request to be processed, it must pass through a server that can handle both protocols. This can be accomplished by making use of proxy chaining which allows the request to be passed from a server that is not able to fulfill such a request (perhaps due to security or networking issues, or its own limited capabilities) to a server that can fulfill such a request.
The first proxy server in a chain will check to make sure a request is valid. If a request is not valid, or not allowed (blocked by the proxy), it will reject the request resulting in the client receiving an error or a redirect. If a request is valid, the proxy may check if the requested information is cached and simply serve it from there. If the requested information is not in cache, the proxy will pass the request on to the next proxy server in the chain. This server also has the ability to fulfill, forward, redirect, or reject the request. If it acts to forward the request then it too passes the request on to yet another proxy server. This process is repeated until the request reaches the last proxy server in the chain. The last server in the chain is required to handle the request by contacting the content server, using whatever protocol is required, to obtain the information. The information is then relayed back through the chain until it reaches the requesting client.
The Squid web caching proxy server
Users configure their web browsers to use the Squid proxy server instead of going to the web directly. The Squid server then checks its web cache for the web information requested by the user. It will return any matching information that finds in its cache, and if not, it will go to the web to find it on behalf of the user. Once it finds the information, it will populate its cache with it and also forward it to the user's web browser.
As you can see, this reduces the amount of data accessed from the web. Another advantage is that you can configure your firewall to only accept HTTP web traffic from the Squid server and no one else. Squid can then be configured to request usernames and passwords for each user that users its services. This provides simple access control to the Internet
In an enterprise that uses the Internet, a proxy server is a server that acts as an intermediary between a workstation user and the Internet so that the enterprise can ensure security, administrative control, and caching service. A proxy server is associated with or part of a gateway server that separates the enterprise network from the outside network and a firewall server that protects the enterprise network from outside intrusion.
Proxy servers receive requests intended for other servers and then act to fulfill, forward, redirect, or reject the requests. Exactly which service is carried out for a particular request is based on a number of factors which include: the proxy server's capabilities, what is requested, information contained in the request, where the request came from, the intended destination, and in some cases, who sent the request.
An advantage of a proxy server is that its cache can serve all users. If one or more Internet sites are frequently requested, these are likely to be in the proxy's cache, which will improve user response time. In fact, there are special servers called cache servers. A proxy can also do logging.
HTTP Server (powered by Apache) has proxy server capabilities built in. Activating these services is simply a matter of configuration. This topic explains three common proxy concepts: forward proxy, reverse proxy, and proxy chaining.
Forward proxy :
A forward proxy is the most common form of a proxy server and is generally used to pass requests from an isolated, private network to the Internet through a firewall. Using a forward proxy, requests from an isolated network, or intranet, can be rejected or allowed to pass through a firewall. Requests may also be fulfilled by serving from cache rather than passing through the Internet. This allows a level of network security and lessens network traffic.
A forward proxy server will first check to make sure a request is valid. If a request is not valid, or not allowed (blocked by the proxy), it will reject the request resulting in the client receiving an error or a redirect. If a request is valid, a forward proxy may check if the requested information is cached. If it is, the forward proxy serves the cached information. If it is not, the request is sent through a firewall to an actual content server which serves the information to the forward proxy. The proxy, in turn, relays this information to the client and may also cache it, for future requests.
Reverse proxy
A reverse proxy is another common form of a proxy server and is generally used to pass requests from the Internet, through a firewall to isolated, private networks. It is used to prevent Internet clients from having direct, unmonitored access to sensitive data residing on content servers on an isolated network, or intranet. If caching is enabled, a reverse proxy can also lessen network traffic by serving cached information rather than passing all requests to actual content servers. Reverse proxy servers may also balance workload by spreading requests across a number of content servers. One advantage of using a reverse proxy is that Internet clients do not know their requests are being sent to and handled by a reverse proxy server. This allows a reverse proxy to redirect or reject requests without making Internet clients aware of the actual content server (or servers) on a protected network.
A reverse proxy server will first check to make sure a request is valid. If a request is not valid, or not allowed (blocked by the proxy), it will not continue to process the request resulting in the client receiving an error or a redirect. If a request is valid, a reverse proxy may check if the requested information is cached. If it is, the reverse proxy serves the cached information. If it is not, the reverse proxy will request the information from the content server and serve it to the requesting client. It also caches the information for future requests.
Proxy chaining
A proxy chain uses two or more proxy servers to assist in server and protocol performance and network security. Proxy chaining is not a type of proxy, but a use of reverse and forward proxy servers across multiple networks. In addition to the benefits to security and performance, proxy chaining allows requests from different protocols to be fulfilled in cases where, without chaining, such requests would not be possible or permitted. For example, a request using HTTP is sent to a server that can only handle FTP requests. In order for the request to be processed, it must pass through a server that can handle both protocols. This can be accomplished by making use of proxy chaining which allows the request to be passed from a server that is not able to fulfill such a request (perhaps due to security or networking issues, or its own limited capabilities) to a server that can fulfill such a request.
The first proxy server in a chain will check to make sure a request is valid. If a request is not valid, or not allowed (blocked by the proxy), it will reject the request resulting in the client receiving an error or a redirect. If a request is valid, the proxy may check if the requested information is cached and simply serve it from there. If the requested information is not in cache, the proxy will pass the request on to the next proxy server in the chain. This server also has the ability to fulfill, forward, redirect, or reject the request. If it acts to forward the request then it too passes the request on to yet another proxy server. This process is repeated until the request reaches the last proxy server in the chain. The last server in the chain is required to handle the request by contacting the content server, using whatever protocol is required, to obtain the information. The information is then relayed back through the chain until it reaches the requesting client.
The Squid web caching proxy server
Users configure their web browsers to use the Squid proxy server instead of going to the web directly. The Squid server then checks its web cache for the web information requested by the user. It will return any matching information that finds in its cache, and if not, it will go to the web to find it on behalf of the user. Once it finds the information, it will populate its cache with it and also forward it to the user's web browser.
As you can see, this reduces the amount of data accessed from the web. Another advantage is that you can configure your firewall to only accept HTTP web traffic from the Squid server and no one else. Squid can then be configured to request usernames and passwords for each user that users its services. This provides simple access control to the Internet
Tuesday, July 25, 2006
Some administration commands
cat /var/log/secure
(as root) Inspect the important system log. It is really a good idea to do it from time to time if you use Internet access.
watch -n 60 my_command
Execute my_command repeatedly at 60-second intervals (the default interval is 2 seconds).
more u can access.
http://linux.about.com/od/linux101/l/blnewbie5_12.htm
(as root) Inspect the important system log. It is really a good idea to do it from time to time if you use Internet access.
watch -n 60 my_command
Execute my_command repeatedly at 60-second intervals (the default interval is 2 seconds).
more u can access.
http://linux.about.com/od/linux101/l/blnewbie5_12.htm
Admin Unix
This blog for System Administrator of UNIX/LINUX.
This wll help u in Technical and Non- Technical Aspect.
This wll help u in Technical and Non- Technical Aspect.
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)
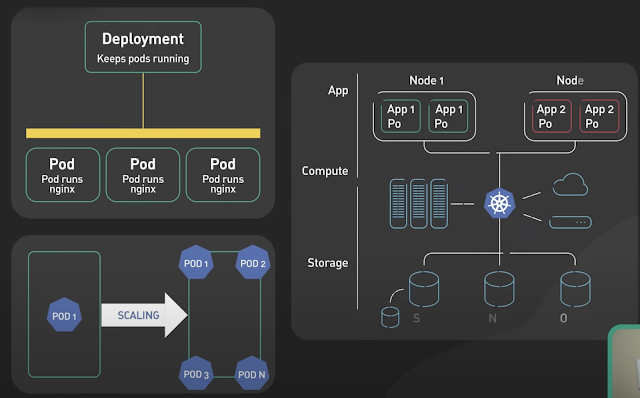
Basics of Kubernetes
Kubernetes, often abbreviated as K8s , is an open-source platform designed to automate the deployment, scaling, and management of container...
-
IOPS (input/output operations per second) is the standard unit of measurement for the maximum number of reads and writes to non-contiguous ...
-
Change Views DEFINER without ALTER VIEW: UPDATE `mysql`.`proc` p SET definer = ‘root@localhost’ WHERE definer=’root@foobar’ AND db=’w...
-
The Unix top command is designed to help users determine which processes are running and which applications are using more memory or process...
